All the information that I will be showing in this POST is an extract of what I cover in this short course! I leave it here for FREE if you are interested!
Chemical Engineering as a Profesional Career

Mathematics
You do not need to be a genius to understand that MATHEMATICS are the main language in which engineers base their knowledge on.
Math will always facilitate our task, specially when we need to make important decisions.
Some examples of common math subjects you will be taking are:
- Algebra
- Calculus I (Derivatives)
- Calculus II (Integrals)
- Calculus III (More Extreme Integrals, Matrixes, Adv. Math, Numerical Methods, Solving Engineering Problems)
Sciences
After Math, of course we need some Sciences!
I like to define the Sciences –> The math that describes our universe.
Common examples:
- Physics
- Biology
- Chemistry (A LOT)
- Inorganic
- Organic
- Electrochem.
- Physical Chem.
- Nuclear

Basic Engineering
Basic Engineering is when, in my opinion, you will understand if Engineering is for you.
Mass Balances

Mass Balance, as the name implies, is the balance of mass (duh…)
It is the foundation of all Chemical Engineering… Why?
Energy balances depend on the total amount of mass/materials going in and out of the process…
Whenever purifying materials, you need: Concentration + Total mass, therefore, the most important part of the plant is the material balance
The sizing of equipment will depend on the total mass flow…
Example: move 100 g of lead, 1000 kg, 1000 ton… yeah, you need different equipment!
Here is a very basic example of what you will learn:
- Block & Flow Diagrams
- Typical Unit Operations
- Non-reactive Mass Balances
- Mass Balance with Reactions
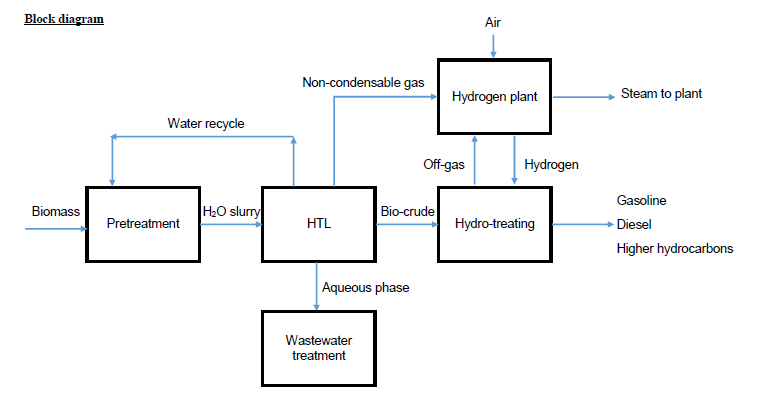
Energy Balances
After mass… then we can get the total energy balance!
Yes… as you can imagine, ENERGY is one of the most important parts of the procedure as it will also dictate:
- Equipment sizing
- Energy $
- Environmental issues

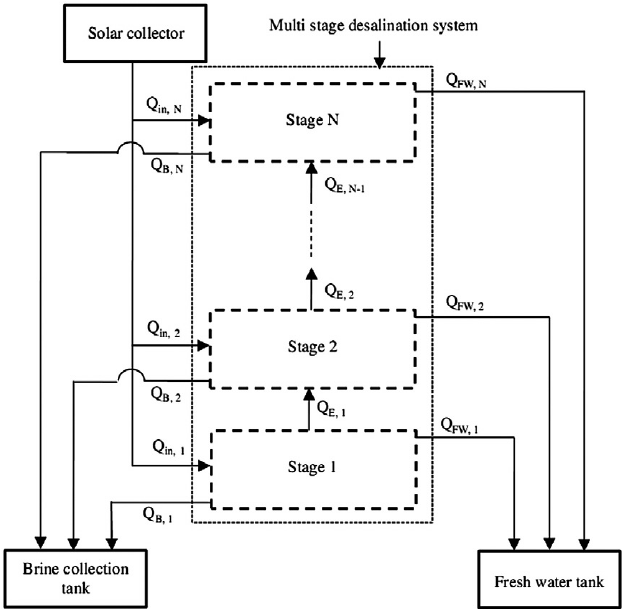
Typical Energy balances that you will be performing:
- Heat (cooling and heating)
- Work via electricity or mechanical
The main concepts:
- Heat/cooling processes
- Enthalpies!
- Isothermal Processes
- Adiabatic Processes
- Balances with reactions
Thermodynamics & Transport
The following subjects explore the nature of the universe in an applicable way.
We explore phases, phase changes, heat, work, machines, heat pumps, engines, efficiency, conversion of energies, transport of properties such as heat (temperature), momentum (velocity) and mass (concentration)
The main idea is to:
- Understand the science behind the natural phenomena
- Design Equipment based on this science
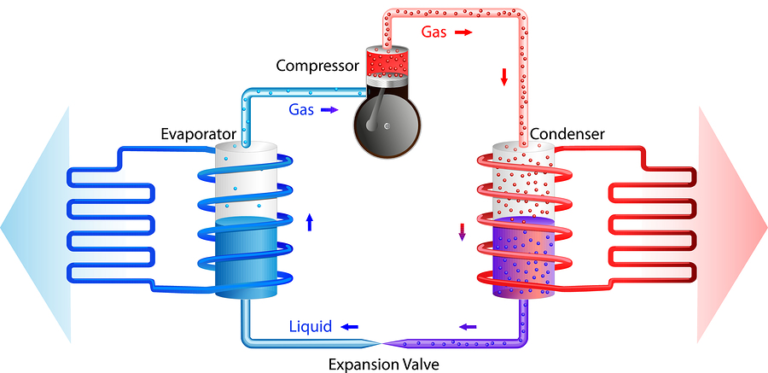
Thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is simple: the study of the interaction of heat and work.
There are many ways in which we can make more efficient processes just by interacting properly between heat and work.
For this, we must further understand substances and their interaction with machines
Common Topics:
- Pure Substances & Mixtures
- Phases, Phase Change, Enthalpies
- Heat Pumps, Engines, Electricity Generation, etc…
- Efficiencies
Transport Phenomena
This subjects explores the nature of property transport… The most common examples:
- Heat Transfer (conduction, convection, radiation)
- Momentum Transport (vleocity profile, mixing, etc, see more below)
- Mass Transfer (diffusion & convection) concentration gradients, etc..

Fluid Dynamics & Statics

Analysis of the FLUIDS (liquids & gases)
- Fluid Dynamics
- Movement of liquids via pumps, pipes, valves, etc…
- Treatment of gases via compressors, fans, blowers, etc…
- Fluid Statics
- Liquid storage
- Pressure exertion
- Gas Pressurization & storing
Unit Operation Design
Unit Operations are very simple: Equipment which will carry either a single/simple task, or multiple/complex tasks
An overview of all common Unit Operations in Chemical & Process Engineering can be studied in this course.
Heat Transfer
Now that you know the “basics” of Thermodynamics & Thermal Machines
- Heating/Cooling, Design of Heat Exhangers
- Reboilers
- Condensers

Momentum Transport
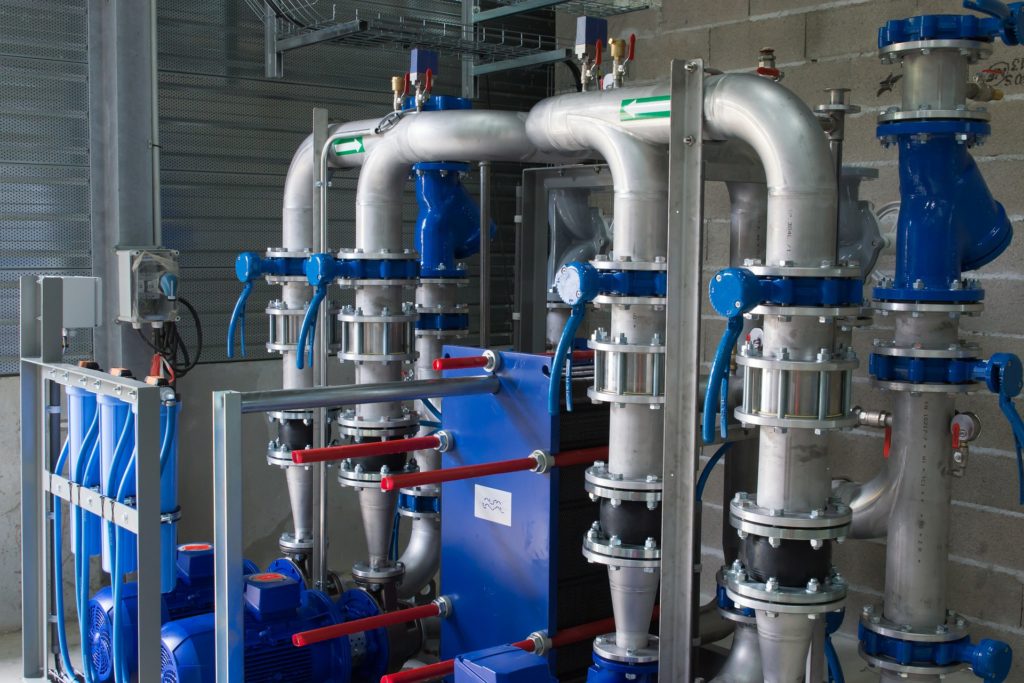

Momentum Transport is essentially working with the following Unit Operations:
- Pumps
- Piping, Fittings & Valves
- Compressors
- Fluidized Beds
- Fans & Blowers
Check out this course which is based in only INCOMPRESSIBLE flow (i.e. liquids)
Separation Processes Technology

Separation Processes AKA Mass Transfer Operations or Units are based in two main tasks:
- Mixing
- Separating/Purifying
We will typically focus in Separation Technologies:
- Gas Absorption
- Binary Distillation
- Liq-Liq Extraction
- Adsorption
- Membrane Tech.
- New Technologies
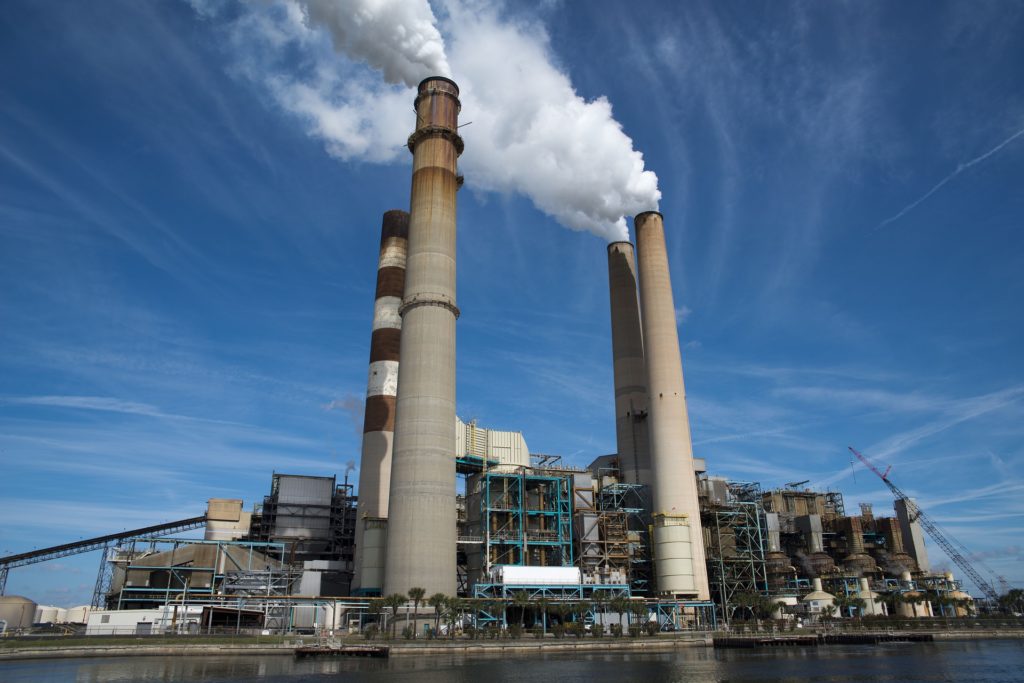

Reactor Engineering
This type of Unit Operation is the ONE that will separate us from the Mechanical Engineers. Note that all previous Unit Operations could be in theory operated / designed by other fellow engineers.
BUT! Chemistry makes us Chemical!
Common Topics:
- Reaction Kinetics
- Reactor Design
- Reactor Operation
- Continuous Stirred Tank Reactors
- Plug Flow Reactor
- Batch Reactor

I really love Reactors!
Check out this Partial Playlist on Reactor Engineering
Plant Design & Control
Once that you know how Unit Operations work and how to design them, its time to make our Chemical Plant!
YES! We need to connect all the little units with pipes and valves! AWESOME!
Plant Design
First, let us learn how to DESIGN a process.
You will need to learn:
- P&ID (Pipe & Instrumentation Diagrams)
- Chemical Process Interaction
- Pricing of Units
- Research & Investment for Chemical Plants

Plant Operation
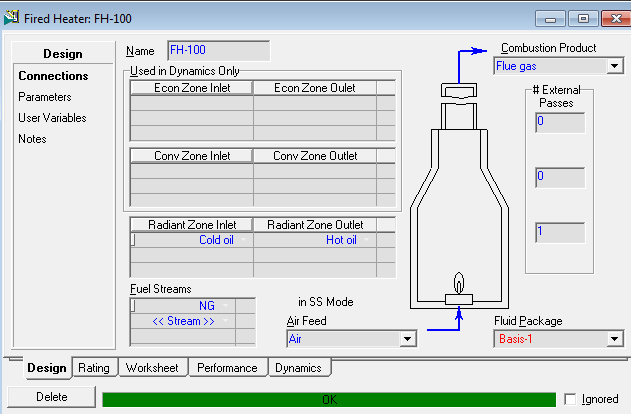
Once you HAVE your plant, it is time to operate it. Learn the typical tasks:
- Shut Down
- Revamping
- Increase/decreasing inputs/outputs
- Start-up a Plant
- Emergency
- Troubleshooting
- Property Control
- Cost Estimation
Control & Automation
We will also need to have “common” practices in the loop control. These are mostly automated so it is important to understand the following:
- Temperature, Pressure, Level, time control
- Stability Theory
- Control Loops
- PID Controllers
- SISO & MIMO theory
- Control Strategies
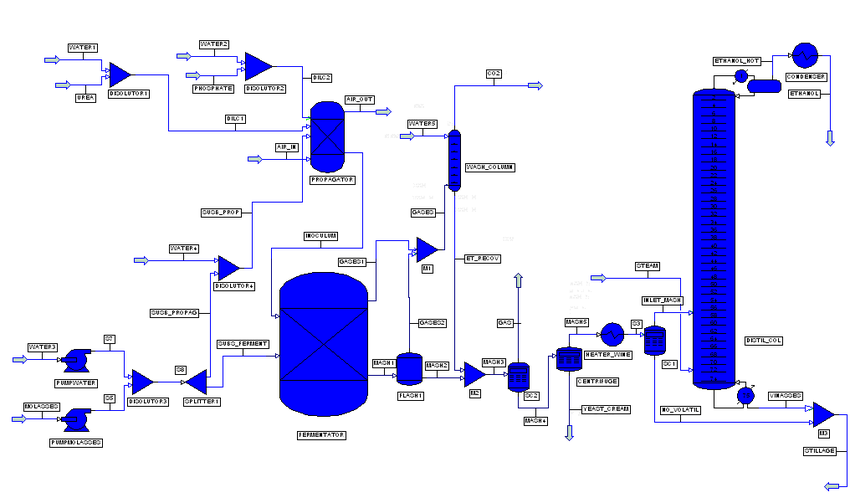
Process Simulation
Make no worries guys! You will NOT be alone in all these last steps… You will be able to model this all by computer! Check this blog post to understand the importance of Process Simulation.
We have several tools, but the most common ones are:
In most cases, you will be working towards the production of X chemical via Y process. You will be modeling plenty of “what if scenarios” in order to verify which one is the best of them and present the final results to your classmates.
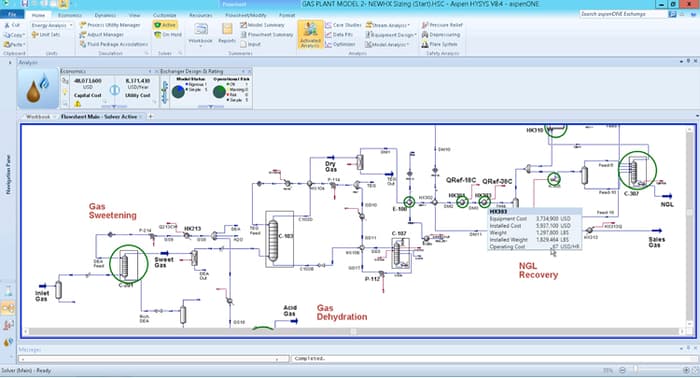
If you are interested in the world of Process Simulation, check out all my Blog Posts related to this (CATEGORY: Process Simulation)
These are some course you might be interested as well:
Those are the most common subjects you will encounter as an aspiring chemical engineer.
Please note that you might find some of those subjects with different names or topics. Some might be blended or eve splitted in several courses , but the main idea is there!
Do you think I missed some CORE chemical engineering subjects? Please let me know in the comment section down below:



